
Generative AI: How It Works & The Use Cases
By Prosanjit Dhar
January 26, 2026
Last Modified: March 13, 2026
Generative AI (GenAI) uses machine learning models to create new content, including text, images, videos, audio, and software code. Unlike traditional AI systems, generative AI creates original content by learning patterns from data.
These models identify and encode patterns in vast amounts of training data, then use that information to understand natural language requests and respond with relevant new content.
The rise of Generative AI
Generative AI became widely known when ChatGPT was released in 2022. It captures global attention and sparks a huge increase in AI development and use.
Today, generative AI includes ChatGPT, Claude, Microsoft Copilot, DeepSeek, Google Gemini, and Grok, as well as text-to-image models like Stable Diffusion, Midjourney, and DALL-E, and text-to-video models such as Veo, LTX, and Sora.
In short, generative AI is now a major part of technology, creating content from text and helping people work faster and more creatively.
How does Generative AI work?
Generative AI development works by training deep learning models on massive datasets and allows them to recognize hidden patterns and structures.
Once trained, these models use advanced algorithms to generate new and original outputs.
Training methods
Generative AI models are typically trained using:
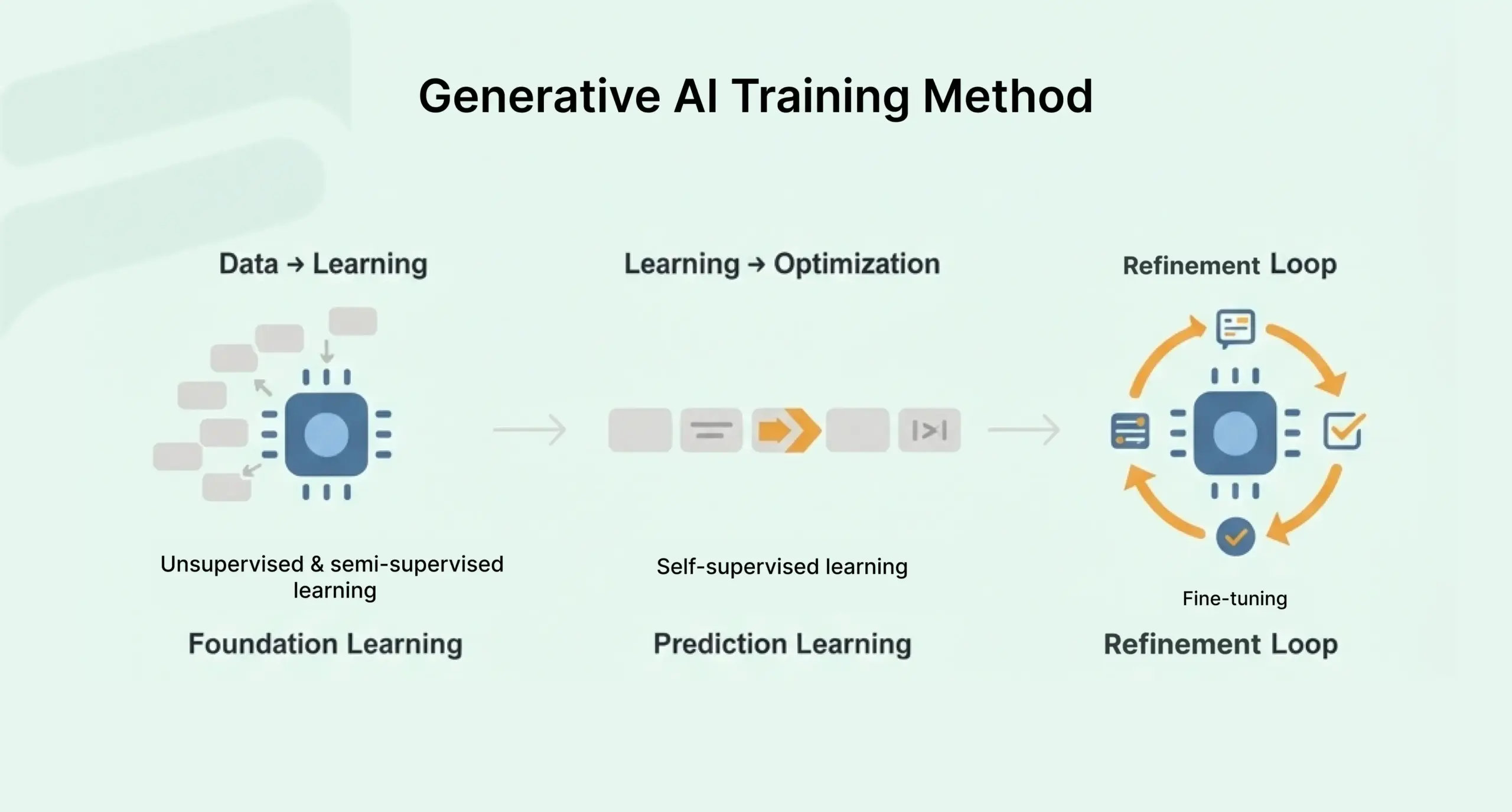
- Unsupervised and semi-supervised learning: This enables the creation of foundation models, which can later be adapted to many tasks (chat, translation, summarization, image generation, etc.).
- Self-supervised learning: For text models, this usually means next-token (word or subword) prediction. After being given a sequence of text, the model learns to predict what comes next.
- Fine-tuning: Developers continually assess outputs and tune models for greater accuracy or relevance, sometimes as often as once a week.
Key Generative AI model types
Different generative AI models use unique training strategies and mathematical frameworks to produce new content. The following model types represent the most widely used architectures in modern generative AI applications.
1. Transformers
Transformers use self-attention mechanisms. This allows them to process entire sequences and capture long-range dependencies more effectively than previous architectures.

Unlike recurrent neural networks that process sequences sequentially, the self-attention mechanism allows transformers to attend to all parts of the input sequence simultaneously.
2. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
GANs consist of two deep learning models: a generator that creates data and a discriminator that evaluates authenticity.
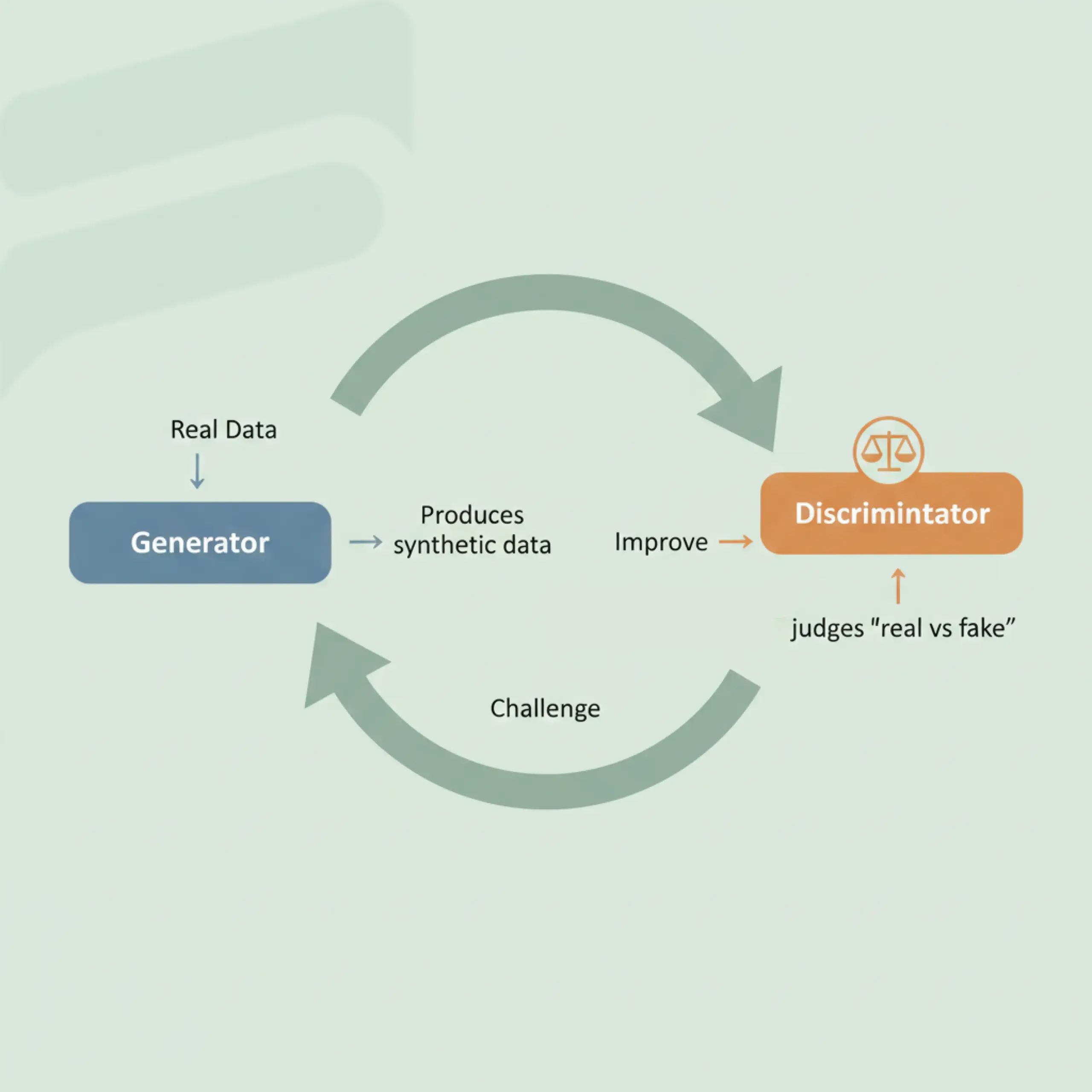
This competitive process improves model accuracy and produces outputs that closely resemble real data.
3. Diffusion models
Diffusion models work by adding noise to training data until it’s unrecognizable. Then, train the algorithm to iteratively remove the noise to reveal the desired output.

While they take more time to train than other models, they offer finer-grained control over output. Particularly for high-quality image generation.
4. Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
Variational Autoencoders compress input data into simplified vectors within a latent space and reconstruct it with variations.
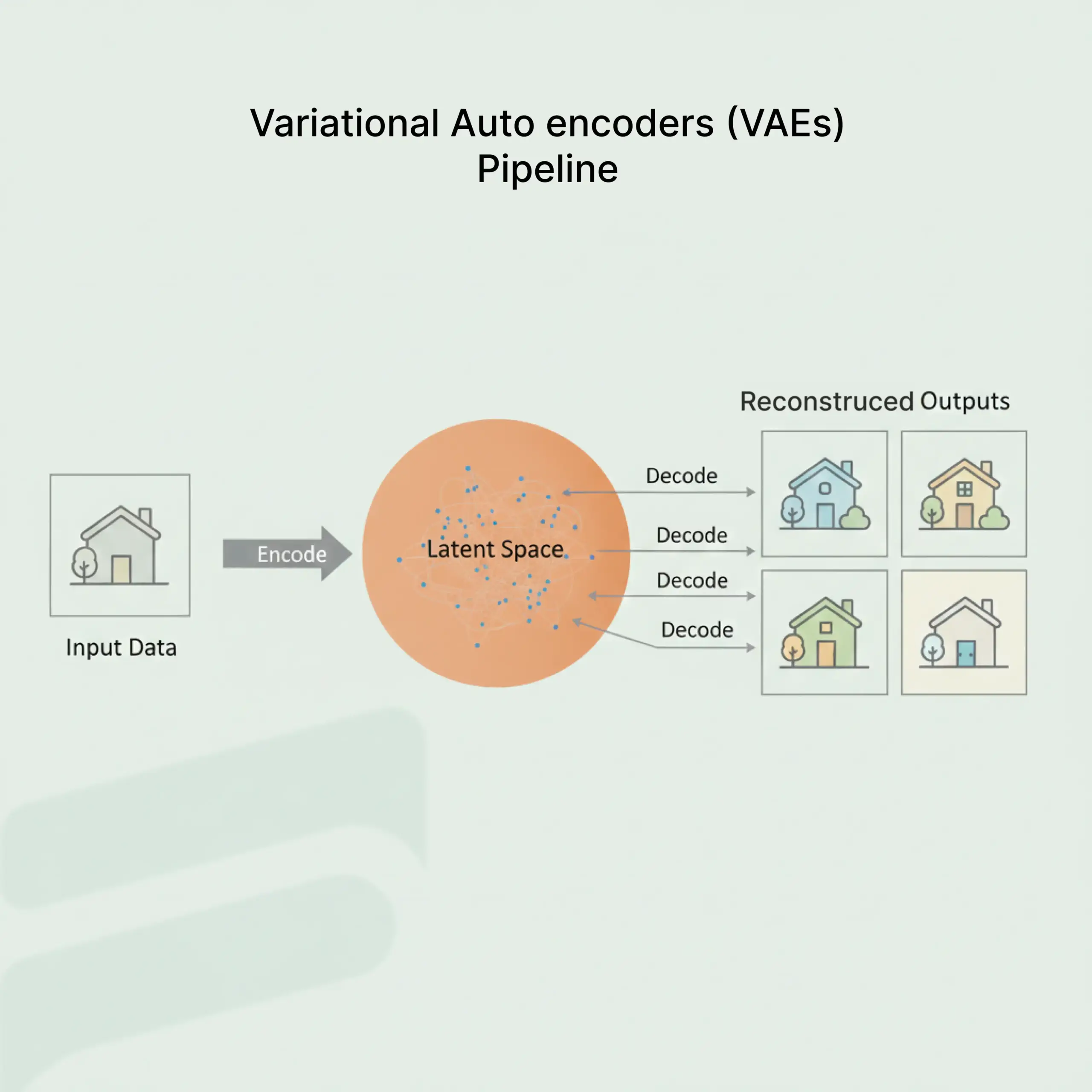
It allows the generation of content that is structurally consistent while maintaining originality.
Popular Generative AI platforms
Several generative AI platforms have become essential tools for automating workflows:
- ChatGPT: A language model based on GPT architecture that generates human-like text, serving as a helpful companion for research, strategy, and content creation.
- DALL-E 3: Generates images from text prompts, enabling creatives to create vibrant illustrations and concept art.
- Microsoft Copilot: Based on ChatGPT and integrated into Microsoft’s productivity suite, also available as a standalone product.
- Google Gemini: Google’s answer to ChatGPT, integrated into Google’s productivity applications and accessible as a standalone chatbot.
Practical use cases for Generative AI
Generative AI can be applied across numerous scenarios:
Content creation
Technical applications
Benefits of Generative AI
Generative AI helps industries scale creativity while reducing manual effort, speeds up workflows, automates tasks, and improves productivity while reducing costs. Key benefits include:
- Speed: GenAI tools work quickly to complete tasks and generate content.
- Multiple use cases: Can be used in various situations, from coding to writing resumes.
- Scalability: Tools are equipped to handle multiple users and tasks without degrading performance.
- Personalization: Creates personalized experiences for users based on individual preferences to enhance engagement and customer satisfaction.
Limitations and challenges
Despite its capabilities, generative AI has several important limitations:
- Requires human oversight: Because GenAI can make mistakes, lacks true understanding, and does not have genuine empathy, it requires humans to review outputs and fact-check information.
- Bias in training data: AI systems learn from existing human-created content, and if that content contains societal biases or prejudices, the AI can absorb and repeat them.
- Privacy concerns: AI systems store user interactions and inputs, and sensitive personal or business information may be shared during conversations.
- Hallucinations: Models remain fundamentally probabilistic tools, and their strength lies in scale and adaptability, not perfect understanding.
Enterprise use cases
Beyond everyday applications, these are generative AI use cases at the enterprise level that show significant business impact.
Financial domain applications
| AI product | Use case | Business benefit |
| Financials assistant | Identify uninvoiced sales orders, create invoices, send to customers, and follow up based on payment schedule | Faster financial closing of books |
| Receivables assistant | Identify uninvoiced sales orders, create invoices, send to customers, and follow up based on the payment schedule | Better cash flow, reduced collection costs |
| Payables assistant | Identify overdue supplier invoices, automate approval of invoices and payments per payment terms | Better tracking of days payables outstanding (DPO) |
| Financial reporting assistant | Identify negative net income trends, automate root cause analysis, create summary and detailed reports with alerts | Automate and reduce time and cost of creating financial reports |
| Financial forecasting assistant | Build financial forecasts, identify anomalies, and underlying causes | Automate financial forecast building and reporting |
| Pricing assistant | Formulate a pricing strategy by analyzing market pricing, internal costs, and competitor analysis | Dynamic pricing ensuring maximum revenue and margin |
Order management applications
| AI product | Use case | Business benefit |
| Field Service Assistant | Assist CSRs with customer history lookup, parts analysis, document management, issue research, configuration, pricing, and quote creation | Improved CSR productivity and customer satisfaction |
| Inside sales assistant | Recommend and personalize offers, upsell and cross-sell based on customer categories, preferences, and purchase history | Increased revenue through personalized selling |
| Customer assistant | Voice-enabled interactions to reduce dependence on humans, classify intent, detect sentiment, and route appropriately | Reduced customer service costs |
| Field service Assistant | Enhance field service engineer efficiency through manuals, virtual/augmented reality, Q&A, digital assistance, and automatic ticket creation | Improved service technician productivity through assistance and on-the-job training |
| Sales query assistant | Retrieve sales and product information using natural language | Eliminate the need to build reports and perform manual analytics |
| Order processing assistant | Create, cancel, and modify orders, perform Available To Promise (ATP) lookups and scheduling, and respond to supply chain changes | Help CSRs decide whether to authorize customer returns or send parts from the parts guide |
| Returns processing assistant | Help CSRs decide whether to authorize customer returns or send parts from parts guide | Increased customer satisfaction |
Concerns and ethical considerations
Generative AI has been used for cybercrime and to deceive people through fake news and deepfakes. Other concerns include:
- Job displacement: Generative AI may lead to mass replacement of human jobs, though a 2025 study concluded that the US labor market had so far not experienced a discernible disruption from generative AI.
- Intellectual property: Many generative AI systems have been described as violating intellectual property laws since they are trained on copyrighted works.
- Environmental impact: Large-scale data centers have environmental impacts, including e-waste, consumption of fresh water for cooling, and high energy consumption, estimated to be growing steadily.
Final thoughts
Generative AI is a powerful tool for both individuals and organizations if used wisely.
However, organizations must balance the tremendous value generative AI can create against the investments it demands and the risks it introduces.
Start off with a powerful ticketing system that delivers smooth collaboration right out of the box.











Leave a Reply