
404 Not Found: Step-by-Step Solution Guide
By Prosanjit Dhar
September 27, 2024
Last Modified: July 17, 2025
A 404 Not Found is part of the 4xx (HTTP status codes) family and the most common error.
It means the web server has received your browser’s request, but couldn’t find any page or resources there.
In most cases, a 404 error appears when you mistype your URL. And, you can just correct the URL to make it work again.
But if not, then you need to follow this guide step-by-step to get rid of this 404 Not Found error.
Let’s start!
What is 404 Not Found?
A 404 Not Found is an error that appears when a web server can’t locate the requested resource. This usually happens when the URL is empty or the provided URL is incorrect.
However, if the URL is correct, the error might be caused by other underlying issues such as broken internal links, deleted or moved pages without proper redirection, incorrect file paths, or even server configuration errors.
And, in case you’re encountering a 404 error, it’s important to identify and fix it early. Because frequent 404 errors can damage your site’s credibility and impact its crawlability by search engines.
But before we dive into solutions, let’s first explore the different forms and types of 404 errors you might encounter.
Forms of 404 errors
404 errors can appear in various forms. Check this list to see if you’re experiencing any of the following:
- “Error 404”
- “404 Not Found”
- “HTTP Error 404”
- “Not Found”
- “Page Not Found”
- “The requested URL was not found on this server”
- “The page cannot be found”
- “We can’t find the page you’re looking for”
Just like different forms, there’re also different types you need to understand in order to fix them effectively.
The difference between hard 404 and soft 404
Search engine bots constantly crawl your website and send signals indicating whether a page returns a 404 error or not.
Based on this exchange of signals, 404 errors can generally be categorized into two types.
Hard 404 error
A hard 404 is the actual HTTP status code for pages that don’t have any resources. When your server doesn’t use redirection, search bots crawl empty pages and receive a clear “404” response code from that page.
This response tells the search bots that the page no longer exists and shouldn’t be indexed.
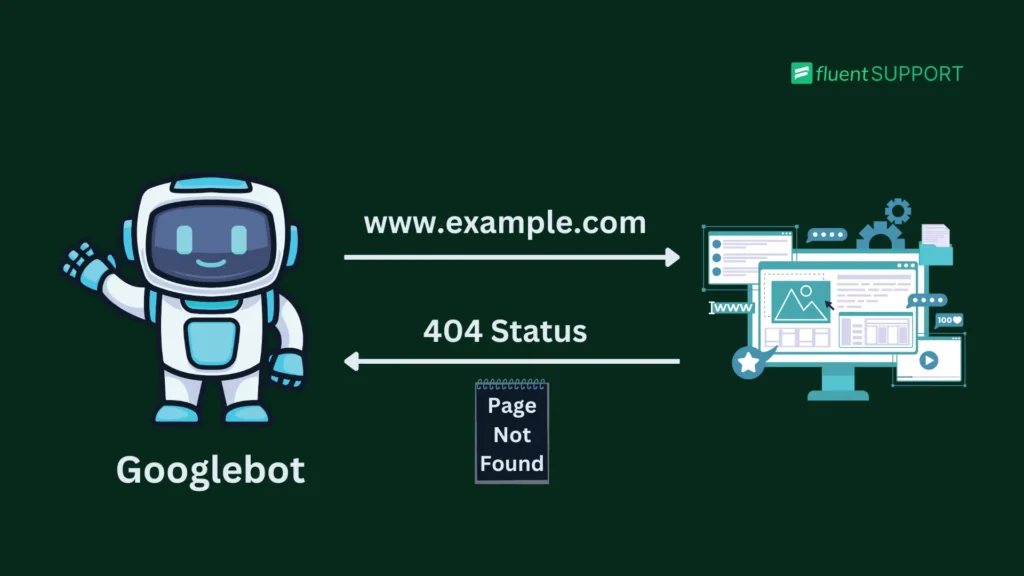
Over time, Google removed the page from search results. This helps crawlers focus on the pages you want indexed, which makes it easier for them to understand your site’s intent.
For example, if you try to access the URL “google.com/find-examples,” you’ll notice that there’s no resource available on the page. This absence means the URL is returning with a 404 status to the web crawlers.
The solution might vary depending on the type or source of the URL.
To check the 404 status yourself, follow these steps:
Open Chrome browser → Turn on the developer tools → Inspect the page → Go to the Network option.
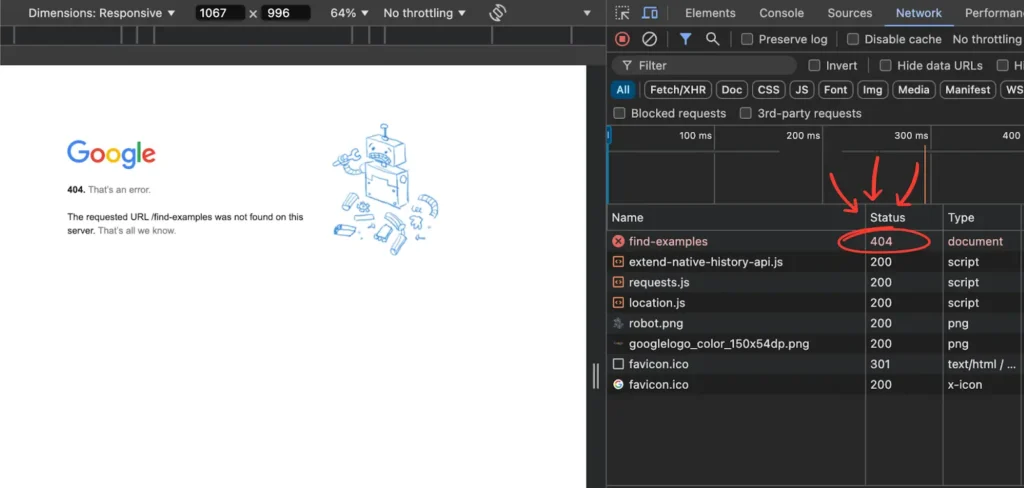
If you don’t see the status immediately, try reloading the page, and it should appear.
Soft 404 error
In contrast, a Soft 404 isn’t a genuine 404 status code. Instead, it’s more of a workaround to transfer the link juice of a blank page. Rather than signaling a ‘404’, the server sends a ‘200 OK’ message to search engines by redirecting them.
This trick made search engines think the page is valid, even when it’s not.
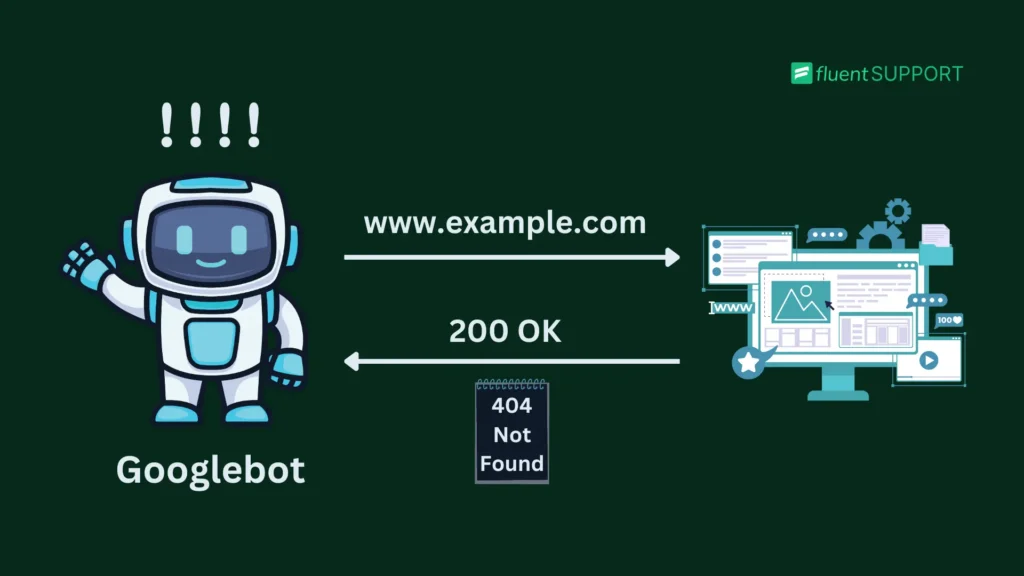
Some webmasters use this method to transfer link juice from a missing page to an existing one.
However, if the redirected content doesn’t match the search intent, it can confuse search engines and negatively impact your website’s visibility.
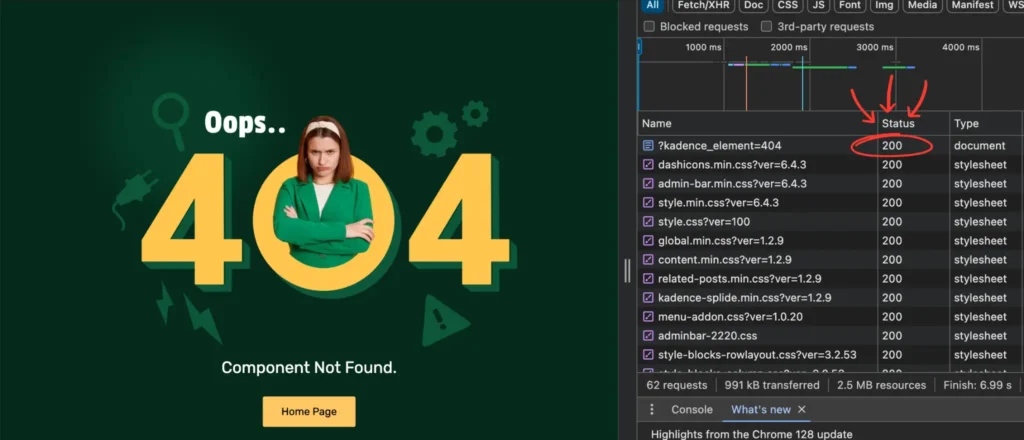
This is often seen with custom 404 pages designed to handle missing pages. Although they display a 404 message to visitors, they technically aren’t a real 404 page since they return a 200 OK status.
The most common causes of 404 Not Found
As 404 Not Found is a widespread website error, the typos also range from simple to complex, which can trigger this issue. Let’s check some of them:
- Moved or deleted page: If you delete or move a page, its URL will become a broken link, and both crawlers and users will see a 404 error.
- Modified slugs: Changing slugs can lead to broken links, causing the old URL to show a 404 error.
- Incorrect URL: This error usually happens when users type a wrong or misspelled URL in the address bar. It can also occur due to plugin errors that affect URL structures.
- DNS misconfigurations: In case the Domain Name System configures to the wrong address, then 404 error codes might appear on your website.
- Cache problem: Misconfigured cache-control settings can prevent browsers or proxies from loading the latest version of resources, leading to 404 errors.
- Missing page assets: Missing page assets like images, CSS, or JavaScript files can also trigger a 404 error.
- .htaccess misconfiguration: Incorrect information in the .htaccess file, such as wrong rules, file permissions, or redirects, can cause a 404 error.
- Check redirects: If you’ve set up redirects, make sure they are working properly. Misconfigured redirects can cause 404 errors.
How to check your website’s 404 error?
The most effective method of checking 404 errors is to use Google Search Console. But there are also some other ways.
Here’s how you can check a 404 Not Found error of your website.
- Use Google Search Console: You can use Google Search Console to track 404 errors if it’s connected to your site. After logging in, go to Page Indexing > Not Found (404) to view a list of all URLs returning 404 errors.
- Check server logs: Check server access logs from Cpanel (/var/log/apache2/access.log for Apache) or (/var/log/nginx/access.log for Nginx) to find URLs returning 404 errors.
- Browser developer tools: Open the developer tools in your browser → go to the Network tab, then reload the page and look for any requests that show a 404 status code.
- Website crawlers: Use web crawling tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to scan your site for broken links.
- Manual testing: Manually enter suspected URLs in your browser. If you see a ‘404 Not Found’ message, there’s an issue with that link.
How to fix 404 Not Found?
As a user, you can try refreshing the page, checking the URL for typos, or trying a different device or browser.
But if none of these work, then you need these advanced solutions below.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to resolving 404 Not Found errors.
Delete or modify URLs from referring pages
To delete or modify a 404 page, identify the source page that tells search engines about the broken link. You can use tools like Google Search Console or web crawlers for this.
Once you’ve found the referring page, decide on the best action based on the issue. If the URL is mistyped, simply correct it.
Alternatively, if the content is no longer available, remove the broken link from the referring page to avoid the 404 error.
Delete old page URLs from the sitemap
Deleting a page from your sitemap depends on the website platform. If you’re using WordPress, just go to the settings of the plugin to manage your sitemap.
In alternative custom-coded sites, edit the sitemap codes manually.
Here’s how to do this for custom-coded sitemaps and two popular WordPress plugins:
1. Custom-coded sitemap editing
For a custom-coded website, you do not need to use any special plugin to edit the sitemap.
Open your custom sitemap (sitemap.xml) file from Notepad or any code editor.
And follow these steps.
- Identify the old page (e.g., https://www.example.com/old-page) from your sitemap.
- Remove the URL from <url> to </url>.
- After deleting that portion of the code, upload the updated sitemap to your server again.
Before
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap-image/1.1">
<url>
<loc>https://www.example.com/</loc>
<lastmod>2024-09-01</lastmod>
<changefreq>daily</changefreq>
<priority>1.0</priority>
</url>
<url>
<loc>https://www.example.com/about</loc>
<lastmod>2024-09-05</lastmod>
<changefreq>monthly</changefreq>
<priority>0.8</priority>
</url>
<url>
<loc>https://www.example.com/old-page</loc>
<lastmod>2023-08-15</lastmod>
<changefreq>never</changefreq>
<priority>0.5</priority>
</url>
<url>
<loc>https://www.example.com/contact</loc>
<lastmod>2024-09-15</lastmod>
<changefreq>monthly</changefreq>
<priority>0.7</priority>
</url>
</urlset>
After
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap-image/1.1">
<url>
<loc>https://www.example.com/</loc>
<lastmod>2024-09-01</lastmod>
<changefreq>daily</changefreq>
<priority>1.0</priority>
</url>
<url>
<loc>https://www.example.com/about</loc>
<lastmod>2024-09-05</lastmod>
<changefreq>monthly</changefreq>
<priority>0.8</priority>
</url>
<!-- Removed the 404 URL -->
<url>
<loc>https://www.example.com/contact</loc>
<lastmod>2024-09-15</lastmod>
<changefreq>monthly</changefreq>
<priority>0.7</priority>
</url>
</urlset>
Google will automatically crawl your sitemap and modify the latest information.
2. Edit the sitemap from Rank Math
If you’re using Rank Math on WordPress, start by navigating to the page editing section in your dashboard. From there, copy the Post ID from the URL.
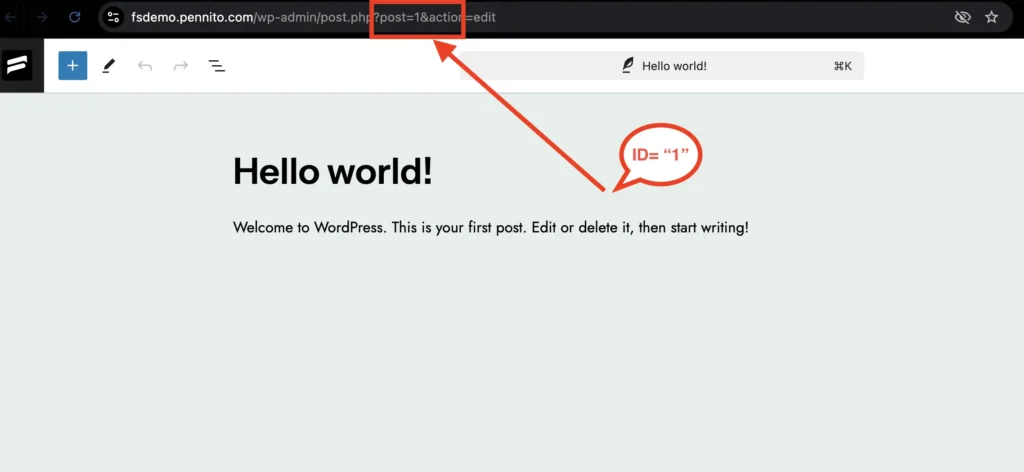
Next, go to the Sitemap settings in your Rank Math plugin. Scroll down until you find the Exclude Posts option.
Paste the Post ID of each post you want to exclude, separating them with commas.
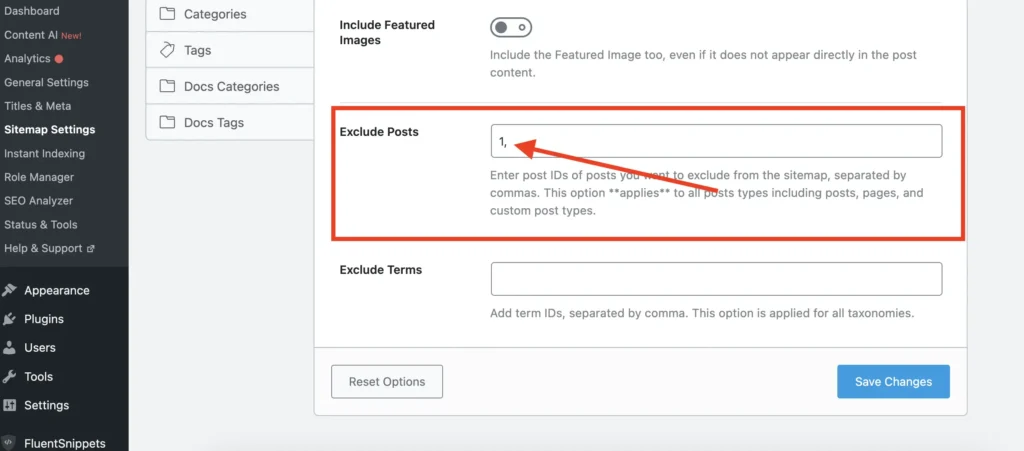
Click the Save Changes button to save the changes. The page will automatically be removed from your sitemap.
3. Disallow search engine for Yoast SEO
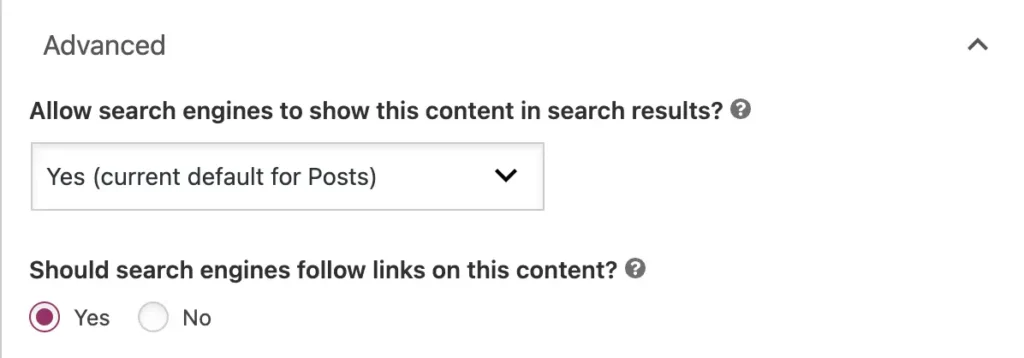
Yoast SEO lets you control crawling permissions for each page. To disallow an empty page, go to the Yoast SEO section in the page editor.
Then, navigate to the advanced options and find the “Allow search engines to show this content in search results?” setting. And, select “No” to prevent search bots from crawling that page.
Configure the .htaccess file
Sometimes, a corrupted or misconfigured .htaccess file can lead to incorrect 404 error codes. You can resolve this issue by removing and regenerating the file. But before that, you need to take a website backup.
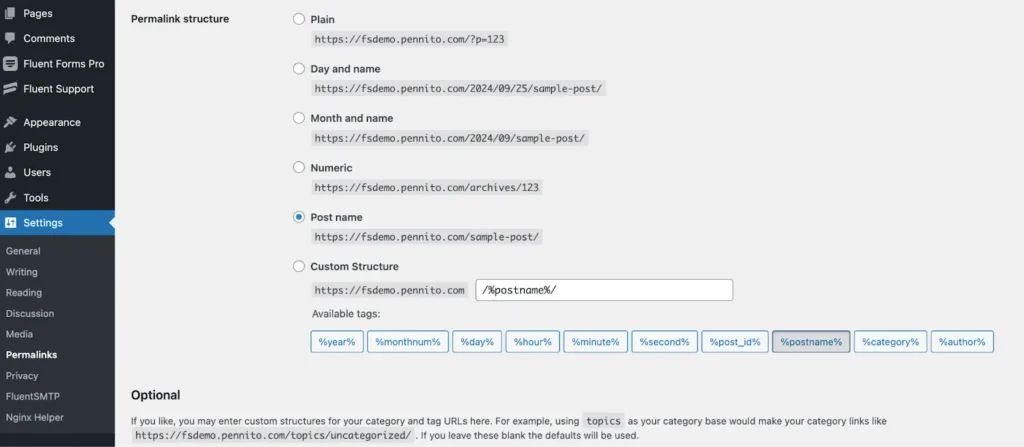
WordPress users can easily fix a malfunctioning .htaccess file by updating the permalinks. Here’s how:
1. Go to Settings in your WordPress dashboard.
2. Select Permalinks and click Save Changes without altering any settings.
This action often resets the .htaccess file and resolves any unusual issues.
In case you’re not using WordPress, access the File Manager in your hosting server and navigate to the public_html directory. Locate the .htaccess file, rename it temporarily, and then rename it back to .htaccess. This will effectively reset the file.
Clear your cache
Sometimes, typos can be surprisingly common. Therefore, start by refreshing the page and carefully checking the URL.
If you still encounter a 404 error, try accessing the link in Incognito mode or on another device. If the page loads successfully, in either case, the issue is likely related to your computer’s cache.
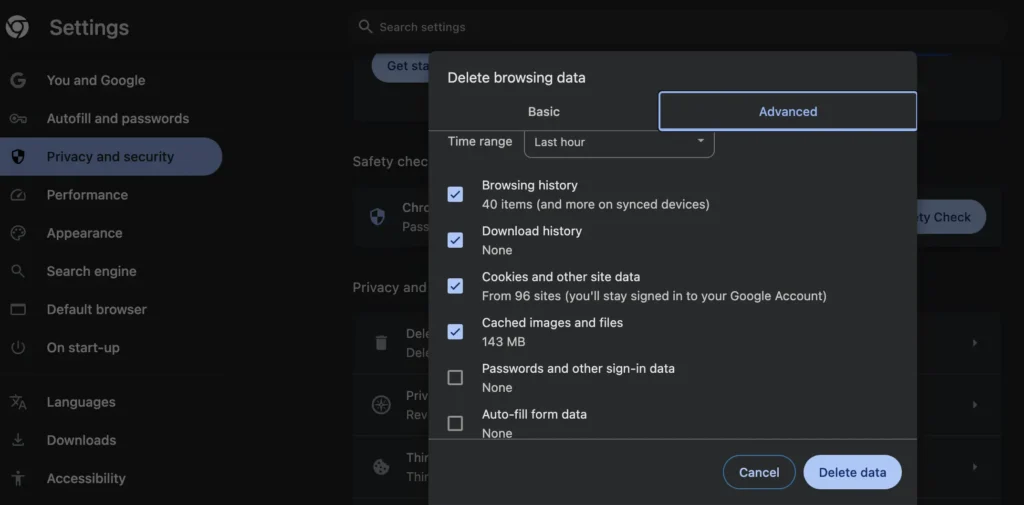
Alternatively, clearing your website’s cache can sometimes help resolve 404 errors. Especially, when these errors are caused by outdated or corrupted cached content being displayed to users.
In WordPress, deleted images, plugins, and other files are often left behind as cached data. These broken files or links can trigger 404 errors or other issues.
To prevent this, use caching plugins like W3 Total Cache, WP Super Cache, or LiteSpeed Cache to regularly clear the cache and keep your website lightweight and error-free.
Set up redirects for 404 Not Found pages
Redirection is a widely used method by technical experts to counter 404 Not Found pages.
But, is it a good idea to redirect your 404 page to your home page or any random page?
The answer to the question is “NO”.
Redirecting an error page like that is generally not a good idea. This technique might have worked in past circumstances.
However, with modern ranking techniques, if external or internal links point to a deleted page that redirects randomly, the potential SEO value of those links is lost.
It’s also misleading for search engines, as they may see this as an attempt to manipulate rankings, which can harm your site’s credibility.
So, be very cautious while choosing a redirect page. If you have a small website with 30-50 pages, we suggest you use the techniques above to solve 404 Not Found errors.
As a new website, you might encounter a few errors that you can fix manually using these techniques. Addressing these issues will enhance your website’s equity and potential.
Alternatively, in big website (website with many pages) cases, it is not possible to counter the vast amount of 404 pages. The numbers can be in thousands. So, you have to use redirects in some specific situations.
Before diving into the typos, here are some redirection plugins that might help you set up 301, 302 redirects, or 404 error tracking.
- Redirection: This popular WordPress plugin helps manage 301 redirects and track 404 errors.
- Rank Math: An all-in-one SEO plugin with a powerful redirection manager and 404 monitoring to fix broken URLs and boost site health.
- Yoast SEO: The premium version of Yoast SEO includes a redirection manager, ideal for handling 404 errors.
- Simple 301 Redirects: A lightweight plugin built to handle basic 301 redirects for sites that don’t require advanced SEO tools.
Now, let’s use redirects for 404 pages.
1. Pages with non-replacement contents
Imagine the 404 error page is completely deleted. There is no similar or relevant replacement content available. In that case, it’s best to leave the page as a true 404. This tells both users and search engines that the content no longer exists.
Or, provide a user-friendly custom 404 page with helpful links or a search bar to guide users to other relevant parts of your website.
A good 404 page should have these features:
- A clear statement that the page the user requested isn’t available
- Advice to help your users correct a possible mistake in the URL
- The main header and footer navigations
- Links to important sections of the website
- A search bar for the website’s internal search function
Here are some examples of custom 404 pages.


2. Pages with replacement contents
Suppose a page has been removed or merged into another page, but you have similar or updated content available under a different slug.
In that case, set up a 301 redirect to the most relevant page that replaces or closely matches the deleted content. This is a permanent redirect that preserves SEO value (link equity) and directs users to relevant content.
For example, if you delete a product page, redirect users to a similar product or category page.
3. Typos or broken links
If a 404 error occurs because of a misspelled URL or broken link, simply set up a 301 redirect to the correct page.
This ensures that users who mistype the URL or click on an outdated link are automatically directed to the correct content.
For example, if “example.com/produc” results in a 404 then redirect it to “example.com/product”. It might show a soft 404 but doesn’t break the search intent and this link equity.
4. Changed URL structure
Sometimes, site redesigning or restructuring can change your URL structure. In this case, use a 301 redirect to guide users to the updated location.
Suppose, the URL “example.com/blog/2023/my-article” is changed to “example.com/articles/my-article”. Use redirection from the old URL to the new URL to preserve link equity and avoid losing traffic.
This is crucial for maintaining both SEO ranking and user experience.
Wrapping up
Unfortunately, the 404 Not Found error is a continuous and persistent issue that you may never fully eliminate. If someone claims otherwise, it’s likely misleading, as users can’t control every mistyped URL.
Therefore, it is best to consistently monitor your website for 404 errors and apply the most suitable solutions from the methods mentioned earlier. By doing so, you’ll be able to improve the customer experience on your website and the health score.
Fix 404 Not Found – FAQ
Here are the answers to some common questions about the 404 Not Found error.
Start off with a powerful ticketing system that delivers smooth collaboration right out of the box.











Leave a Reply