AI Agentic Workflows: What They Are & How to Build Them
By Uttam Kumar Dash
September 22, 2025
Last Modified: November 13, 2025
Automations in workflows are changing fast. Old rule-based systems are getting replaced by AI agents that think, plan, and adapt. Agentic workflows lead this shift because they move beyond simple “if-then” logic to systems that reason through complex problems.
What is an agentic workflow?
Agentic workflows are AI-driven processes where intelligent agents plan, reason, and act toward specific goals with little human input. They use tools, memory, and self-checks to adapt as conditions change, producing flexible and context-aware results that improve efficiency.
Think of it as having a digital assistant that can make decisions. The agent doesn’t just follow instructions. Instead, it actively figures out the best way to reach its goal.
An agentic workflow has several key traits:
- Agents make decisions within set limits
- Paths change based on real-time data
- Built-in checks catch and fix mistakes
- Multiple tools work together smoothly
This creates a big shift from reactive to proactive systems. Rather than waiting for triggers, agentic systems constantly check their environment. They adjust their strategy based on what they learn.
How to implement AI agentic workflows
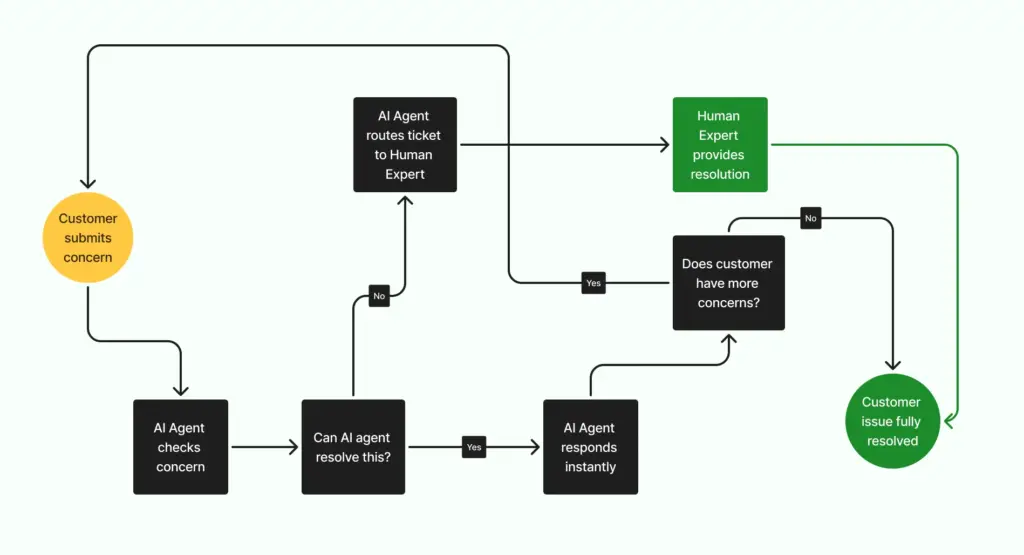
Success begins with choosing the right first project. Start small instead of trying to automate everything. The best candidates are simple, repetitive tasks where people gather information, and customers wait for updates. Automating these cases shows quick value while keeping risk low.
Before building, set boundaries to stay in control:
- System access: Which platforms or databases can the agent read?
- Allowed actions: What is safe for the agent to do on its own?
- Escalation rules: When should it hand over to a person?
- Success metrics: How will you measure results?
Oversight is critical. Begin with human approval for every response. As the agent proves reliable, you can grant more independence. Tracking is just as important. Keep an eye on:
- Accuracy and error rates
- Escalation frequency
- Resource usage
- Customer satisfaction
These insights show what works, where mistakes happen, and how value grows.
You do not need heavy systems to begin. A contained case like ‘Order Status Inquiries’ is enough. Staff often check multiple systems to give a simple answer, so automation saves time and creates consistency. If your team deals with password resets or invoice checks, you can follow the same process with those tasks.
1. Pick your battle wisely
It is best to start with a process that frustrates your team every day. Order status inquiries work well because they require pulling information from several systems, yet the customer only needs a clear update. Since the scope is limited, you can experiment without risking major disruptions.
2. Map your agent’s world
Before building anything, define what your agent can see and do. For order status inquiries, it should have read access to the order database, the shipping carrier’s API, and payment records. Limit its actions at first.
Let it gather data and draft responses while a human approves the final message. You should also set escalation rules. For example, escalate automatically if the order value is high or the confidence score drops too low.
3. Build your minimum viable agent
Begin with the simplest version that creates value. Most teams use workflow tools such as Zapier, n8n, or Microsoft Power Automate, paired with an AI service. Connect your systems and provide a clear prompt. For example:
You are a customer service agent handling order status questions.
Customer: [name, account type, history]
Order: [number, items, dates, current status]
Shipping: [carrier, tracking, estimated delivery]
Respond with:
1. Current order status in plain language
2. Expected delivery timeframe
3. Any required action such as refund or replacement
4. Confidence score from 1 to 10
If confidence is below 7 or order value exceeds 500 dollars, escalate to a human.
This way, the agent focuses on one problem and does it reliably.
4. Add reflection and quality control
Your agent should check its own work before moving forward. It can generate a confidence score and pause when the score is low.
It should also compare proposed actions against company policies and run basic error checks, such as verifying that tracking numbers are valid. Finally, human agents should review drafts quickly before they go to customers.
5. Deploy with oversight
At first, learning matters more than efficiency. Run the agent in shadow mode so it generates responses without sending them directly.
Humans review and send replies, while you track logs, scores, and timings. This allows you to measure performance without affecting customer experience.
6. Refine and expand
Once you see results, refine the system with real cases. Update prompts based on failures and add examples. If order status works well, you can extend to related tasks like shipping delays or returns. Increase autonomy slowly.
Start with automatic replies for simple cases while keeping human review for complex or high-value ones.
7. Keep it sustainable
Treat the workflow as a living system. Review results regularly, document what works, and test model updates carefully before production.
Train your human agents to work with the AI by reviewing outputs and providing feedback. This ensures the collaboration keeps improving over time.
Tips: Start with a simple flow like order status inquiries, refine it based on real-world use, then expand step by step. The same procedure applies to other repetitive tasks, so you can adapt it as your team’s needs evolve.
Agentic workflow vs traditional workflow
The main difference lies in how each workflows handle uncertainty. Traditional workflows follow rigid decision trees that work best for predictable tasks. And, agentic workflows use AI agents that can adapt, plan, and choose actions based on context.
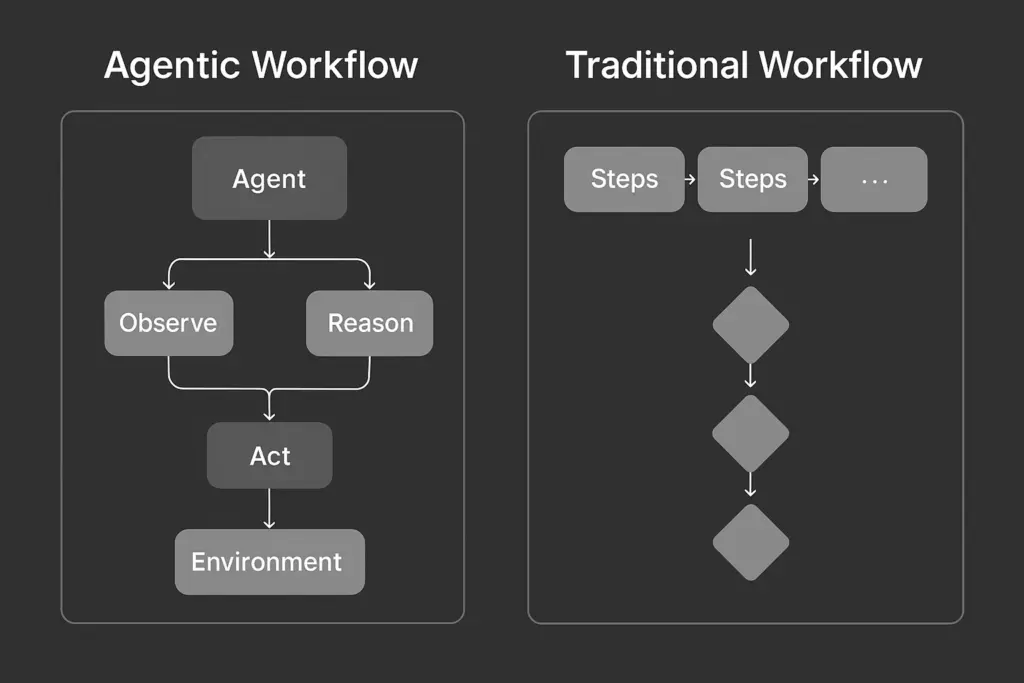
This makes agentic workflows better suited for dynamic situations such as customer service, where personalization and flexibility are essential. On the other hand, traditional workflows are for stable processes where the steps rarely change and consistency matters more than adaptability.
| Aspect | Traditional Workflows | Agentic Workflows |
| Core approach | Predefined decision trees with rigid branches | Adaptive reasoning by agents that can plan and choose actions dynamically |
| Best suited for | Stable, predictable processes (e.g., invoice approvals) | Messy, variable situations where context changes |
| Response to unexpected events | Often fail or escalate directly to a human | Gather more data, make informed guesses, and continue within safe limits |
| Customer service example | Examine the customer’s problem, review history, check policies, and craft a personalized solution | Examine customer’s problem, review history, check policies, and craft a personalized solution |
| Maintenance needs | Requires constant updates for new scenarios | Adapts reasoning to novel cases within its capabilities |
| Scalability | Scales well only if processes don’t change often | Scales by handling a wide range of conditions without needing frequent reprogramming |
Components of agentic workflow
Four main parts work together to create intelligent workflows. Understanding these pieces helps teams build better systems.
- Planning component: This breaks big goals into small steps. It puts them in logical order. Advanced planners can create backup plans and pick the best option based on current conditions.
- Memory systems: These store information across different interactions. They remember past decisions and outcomes. This helps improve future performance. Memory makes agentic workflows different from basic automation that starts fresh each time.
- Tool integration: This gives agents ways to interact with other systems. It includes APIs for getting data and connections for storing information. The agent coordinates these tools to complete tasks across multiple platforms.
- Reflection mechanisms: These provide quality control. Agents can check their own work before taking action. They catch errors and verify that decisions match company policies. They also figure out when humans need to step in.
Real-life examples of agentic workflow
Companies across different industries are using agentic workflows to solve real problems. These examples show what’s possible and the results you can expect.
- Financial services: A major bank built an agentic system for loan applications. The agent examines each application and pulls credit reports. It verifies employment information and checks all regulatory requirements. Processing time dropped from days to under four hours. Compliance standards stayed high while applicant experience improved significantly.
- SaaS company: A growing software company deployed agents for billing questions. The system analyzes customer accounts and investigates payment problems. It reviews discounts and finds the root cause of billing issues. Human escalations dropped by 40%. First-contact resolution rates improved along with customer satisfaction scores.
- Healthcare organization: A medical group uses agentic workflows for patient intake. The system reviews forms and spots missing information. It checks medical histories and verifies insurance coverage. Routine cases get handled automatically, while complex medical situations go to clinical staff.
- eCommerce platform: An online retailer built agents for order fulfillment. The system analyzes inventory levels and shipping costs. It considers delivery times and customer preferences. Orders get rerouted when needed. Customers receive proactive updates about delays or alternative products.
Wrapping up
Agentic workflows solve the problems that rigid rule-based systems can’t handle. They provide flexibility for complex processes while maintaining the reliability businesses need.
Success comes from starting small and scaling thoughtfully. Pick processes with clear value and measurable results. Build proper safeguards and keep humans involved where judgment matters most.

Frequently Asked Questions
Get clear answers to common questions about agentic workflows.
Start off with a powerful ticketing system that delivers smooth collaboration right out of the box.










Leave a Reply